
BLOG

BLOG
With ‘Anonymous’ on the loose, the trip to much-covered secrets of various royal families and police departments were dug and uncovered. Such incidents often bring up the question of data security. With the state of ‘data, data everywhere, not data to be left unsecured’, the priority is on digital security.
With the pace at which smartphones are spreading worldwide, we have no choice but to ensure that our ‘digital mates’ are iron-clad regarding data security. In the Bring Your Own Devices (BYOD) era, software is the major asset. No application vulnerability is tolerable, and this is where the mobile Security Development Lifecycle comes into play.
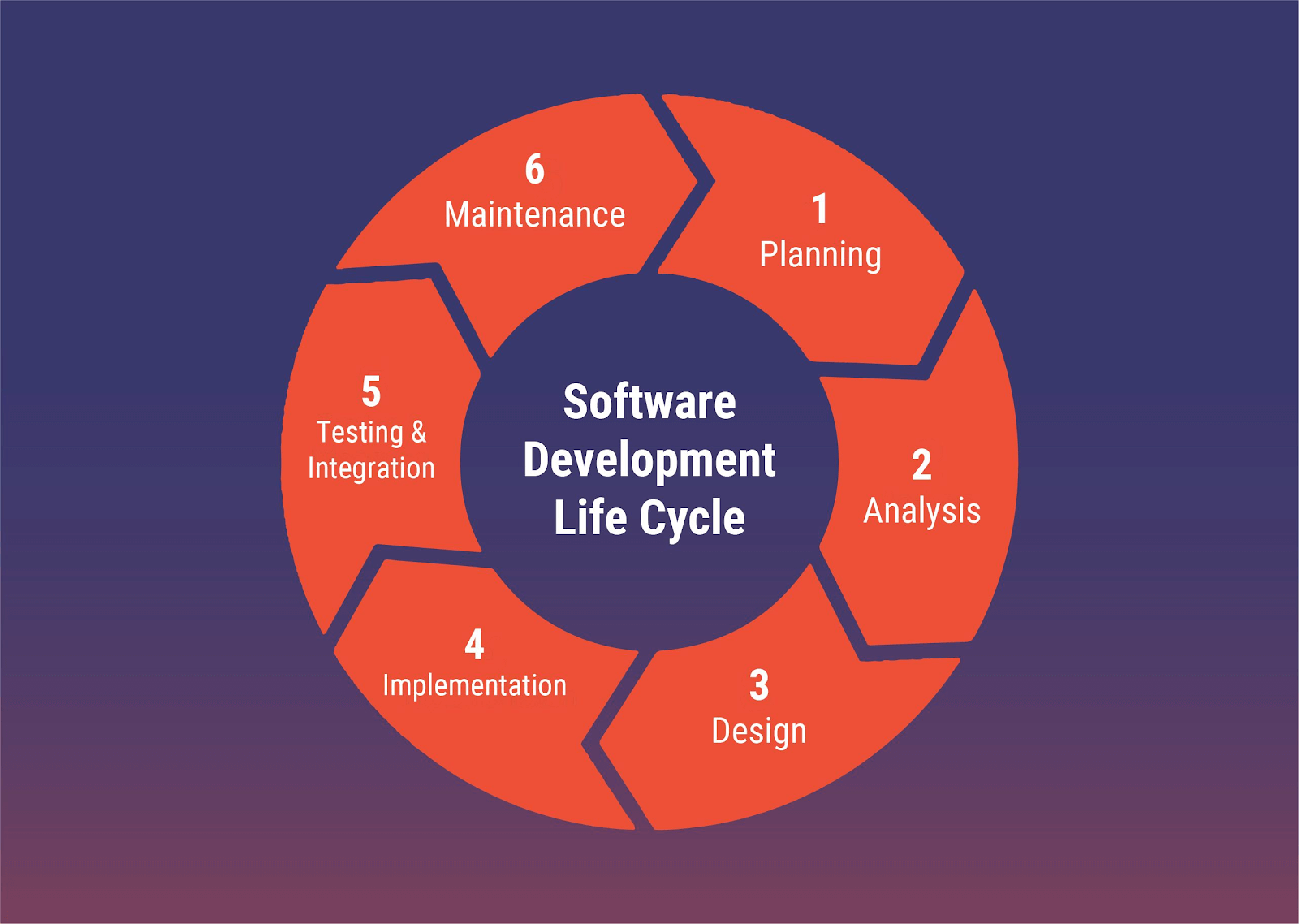
The mobile security development lifecycle or SDLC is the procedure for benchmarking the best security practices for the mobile device in question. All that needs to be done is:
These activities are then implemented. The SDLC involves mainly 4 phases -
Security-related activities are added to the existing development procedure. The phases include -
This phase comprises
This phase zooms in on the project-scope and the outputs comprise -
The focus now shifts to listing the requirements of the project.
a) The IT team assembles and takes into account all the requirements of the project as put on by the SMEs or Subject Matter Experts and the brand stakeholders.The output of this phase varies based on whether the preferred methodology is Agile or Waterfall -
There is also the step of third party software tracking that is initiated by the senior technic at the lead.
Now that the list of requirements is planned out, it is time for the design process to commence.
The outputs of the designing and prototyping include -
are listed out in the design documents and are used for development as the commencing point.
The development phase is a crucial part of the Security Development Lifecycle or SDLC.
a) Threat modeling updates are listed for static analysis by the developers and the QA or the security expert in the team.
b) The security design is reviewed by the development team and the scanning of the vulnerability is conducted by the security experts and developers.
c) The codes are also reviewed by the team of developers for the project.
Testing is the most important phase of the SDLC because without testing implementing the security measures is very risky. The phase includes -
a) Fuzzing is initiated by the QAs and the team-developers
b) Dynamic analysis is carried out for security reviews by the team of security experts
c) The test for third-party penetration is conducted by the certified pen testers for third-party
A number of releases are carried out in this phase -
a) Final gap analysisThe last phase of the SDLC, the sustaining part comprises -
a) Tracking and reviewing of third-party software that is initiated by senior technics or technical members at the lead.The SDLC has diverse benefits that are listed out below -
SDLC boosts the need to abide by the security-related regulations and laws. In case these regulations are neglected, the resultant may be penalties and fines.
Considering that SDLC monitors vulnerabilities, the output is nose-diving trade-risks and enhanced quality of applications.
With the practice of the SDLC, attention is paid to any flaw at its primary stage. Thereby, there is significant mitigation in the cost involved in detecting and fixing the bugs.
Cyber-attacks often rest in considerable damage to your trade that has a similar effect on the revenue-generation, client credibility, and business standing. This can be prevented by SDLC practices.
Trusted and certified platforms are put to use by service providers as foundations. On these platforms, new value-added services are built to ensure boosted trust.
With certifications, multiple doors are opened for the vertical and geographical markets.
Security is a major leverage during the selling of products for both developers and manufacturers. Tailored evaluations without detailed specifications establish the credibility of the brand for prospective clients
Despite the leverages that SDLC offers, enterprises often miss out on it considering that they have limited knowledge about the best practices for the cycle. Here the highlighted practices that will help boost the security -
The manual analysis of the traffic that flows from the app to a web server is essential. For this, mobile devices communications need to be encrypted to prevent any chances of interception. Employing security practices on the path between the mobile and web server ensures that all the sensitive information is well-guarded when you go for app development.
Although OS and device manufacturers offer security measures from time to time, they cannot be trusted enough. On the contrary, one should take into account mobile security from the application level. This mitigates the platform-dependency.
Hiring credible organizations to audit applications are essential. Mobile applications when putting through manual penetration testing and automated tests are a crucial practice.
Protecting sensitive information of the corporate sector is called containerization and is a technique to store the data in a separate container in mobile apps.
That’s some of the best practices for SDLC. However, what do you do if you have already implemented security measures and need to mend them? Here are a few secrets that are taken up by pros in the mobile SDLC mending process
The world of mobile is facing new waves of changes. This is well showcased by the foldable smartphones that were launched in 2019. However, the mobile marketplace is still fractured owing to the peaked malware threats. This makes it essential for mobile application developers to manufacture secure apps. It calls for the implementation of the following mending-secrets into the procedure which has been listed out below -
As an essential part of up-front steps are -
One can also use SDK to manage the components that are required in this context.
Secure user communications have become a forgotten story. Like a domino effect, there have been cases of insecure applications. In this case, internal applications and APIs can be considered as examples. Despite blocking all means of access and making them available only on an internal network, that is not secure enough. Measures need to be taken accordingly.
Portfolio companies can view or treat the mobile app security requirements as non-functional while in the primary phases of application development. This means -
.png?width=750&name=pasted%20image%200%20(1).png)
It always serves better to open up your agile boards to your brand’s security team. With certain platforms, development stories need to be flagged as high-priority or risk factors. In multiple brands, security resources are stretched. Hence, the flagged out stories (as mentioned above) fetch the attention of your enterprise’s security team prior to your app hitting GA (General Availability).
Resolving authorization or authentication early on in the agile development cycle is crucial. This prevents any chances of confusion between the two. This means looking into the -
With mobile application testing, the best step is automation and in this case, the following are recommended -
that test the common vulnerabilities (like SQL injections). The next step would be to automate tests against the requirement of -
These testings are conducted
Tests can be augmented by the end of each sprint with MAM (Mobile Application Management). This approach has often been pursued to test how their mobile applications interact with the internal business proceedings and its infrastructure. Such testings help clients fix -
Sans the SDLC,
With so much on the line, brands stepping into the mobile realm need to look into the SDLC front and ensure that the best practices are taken to mend it. This would have a significant impact on the sale of products and the credibility of the brand in question.
