BLOG

BLOG
The NIST cybersecurity framework is a set of guidelines and best practices to help organizations improve their security posture. The recommendations and standards allow the organization to be better equipped to identify and detect cyberattacks and provide guidelines for responding, mitigating, and recovering from cyberattacks.
In this guide, we discuss everything from the core functions of the NIST framework to how Appknox can help you automate NIST compliance management. So, let’s dive right in.
|

The NIST framework helps organizations make security adjustments to ensure alignment with the ever-evolving threat landscape and the sophistication of attacks. The uniform set of rules, guidelines, and standards act as a top-level security management tool for establishing a cybersecurity program to assess risks.
These guidelines are globally followed by organizations of all sizes and niches, from manufacturing to government agencies, healthcare, and more, to secure their cybersecurity posture.
It's important to note that adherence to NIST compliance remains voluntary, which allows organizations to customize the guidelines according to their needs to strengthen their security posture. However, compliance is mandatory for companies and contractors dealing directly with federal agencies.
Over the years, NIST has published specific guidelines and requirements for different industries and businesses. For example, any contractor working on government contracts should usually abide by “special publications” like NIST 800-53, which deals with privacy and data security controls. On the other hand, NIST 800-171 deals with protecting classified information protection.
Private-sector companies that do not deal with government agencies need not mandatorily follow NIST guidelines.
However, complying with the NIST framework provides numerous benefits, enabling organizations to better protect their cybersecurity infrastructure.
NIST compliance encompasses several standards and guidelines, which can be broadly categorized into three types.
|
Types of NIST compliances |
Goal |
What it consists of |
|
NIST 800-53 |
Supports organizations in complying with the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) |
110 requirements in 14 categories, including access control, security training, incident response, and audit log system |
|
NIST 800-171 |
Protection of controlled unclassified information (CUI) |
Access control, risk assessment, security assessment, system and communications protection |
|
Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) |
Identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover |
Catalogs of cybersecurity outcomes based on specific guidelines and practices |
Let’s understand the core components of NIST compliance required to build robust cybersecurity programs.
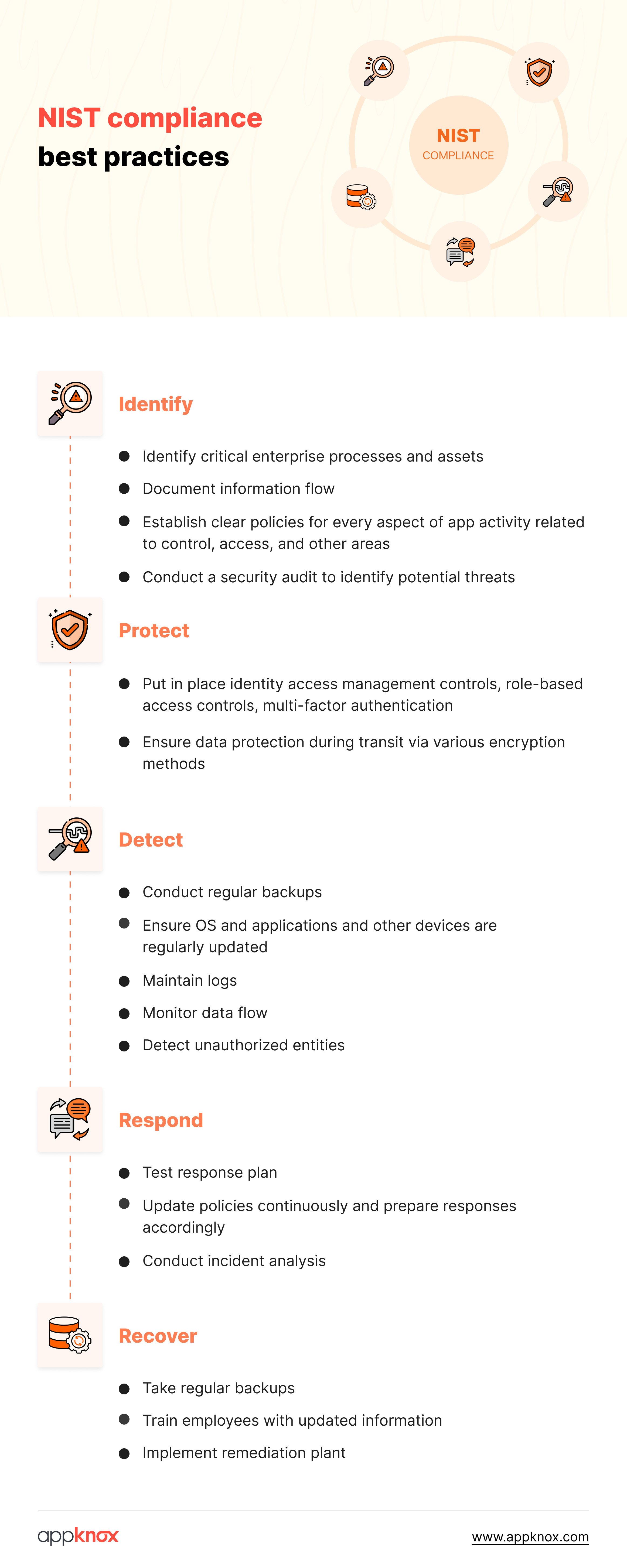
The NIST compliance framework is exhaustive, covering 23 categories and 108 security controls. These compliances fall into five core functions.
|
Core Functions |
Goal |
Categories |
|
Identify |
Assess and uncover threats to systems, assets, and data |
|
|
Protect |
Implement necessary controls to identify assets |
|
|
Detect |
Take steps to detect vulnerabilities |
|
|
Respond |
Control and mitigate cyber threats |
|
|
Recovery |
Implement processes to restore asset capabilities |
|
The NIST framework is intricate and comprehensive; obtaining NIST compliance certification requires thorough preparation and certification.
Though NIST doesn’t officially certify contractors and vendors, they must pass the audit tests conducted by third-party accredited bodies like the National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP).
Here’s the step-by-step process:
When preparing for NIST compliance, evaluate your organization’s security posture and infrastructure.
Answer these questions to determine the NIST standard to apply. For example, NIST CST is the foundation of other controls. If your organization has this in place, the next step would be looking to NIST 800-53 to fill the gaps.
Create an inventory of your systems by documenting the current information systems in your organization, including hardware, software, and network resources. This helps identify vulnerabilities and understand the security measures needed.
Categorize the information your organization handles based on its sensitivity. Ask yourself, “Why do I need this step in the NIST compliance audit?”
This step helps you prioritize security efforts by allocating resources for critical tasks to protect essential information.
The identification phase of risk management involves recognizing the threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise your organization’s data. They include physical and online environments such as cyber threats, internal vulnerabilities, or outdated or broken cryptographic parameters.
Ensure your identification process detects new risks immediately as they arise.
Post risk and vulnerability identification, scrutinize the severity of risks to their assets and operations. Prioritize risks according to their severity and allocate resources to meet the most pressing concerns.
The mitigation step of NIST compliance involves creating safeguards to limit the potential damage in case of a data/security breach. Plan contingency strategies that defend the organization against malicious actors and allow rapid recovery and adjustments for emerging and evolving threats.
User identification controls are a part of access control in the NIST compliance framework. This ensures every individual accessing your system and hardware is identified for accountability and tracking. It creates transparency with user activities and protects against security breaches.
Authorization and access management safeguards critical information from misuse by restricting or giving role-based access to internal and external parties.
The incident response policy is a blueprint that outlines the roles and responsibilities expected during a security breach.
The policy guides the organization’s responses to limit the damage and decrease the recovery time while mitigating the potential ramifications.
Deploying systems to detect anomalies and security breaches will allow you to make swift decisions to contain the threats.
Documenting the incidents and their preventative measures helps your team fortify the infrastructure against further attacks. Keeping an actionable incident response empowers your organization to build resilience against cybersecurity threats.
Use frequent security assessments to identify gaps in the system’s security controls and target key areas susceptible to vulnerabilities while meeting regulatory guidelines.
Once the assessment policies are in place, test the existing security controls using manual and automated pentesting to simulate potential threat scenarios against possible attacks. This step maintains an up-to-date security posture in the NIST compliance framework and helps your systems adapt to changing threats.
WRemediation actions are an integral part of NIST compliance, as they target and correct identified vulnerabilities to strengthen weak spots and protect the mobile application from potential breaches.
A proactive approach during the NIST compliance assessment improves security infrastructure with vulnerability patch management.
The NIST framework applies to all U.S. government federal agencies and software and mobile application providers who support them.
Like all software, mobile apps contain vulnerabilities (either due to errors in design or implementation or malicious intent) that can expose the user, mobile device, and its data or services to attacks.
They include:
Vetting mobile apps for NIST compliance before deployment on user mobile devices allows the administrator to help detect software or configuration gaps that may create vulnerabilities capable of violating security or privacy policies.
Automated and manual testing looks for evidence of different types of malware and mobile application security threats.
Appknox specializes in mobile app security, and in the NIST compliance framework context, it helps reduce the overall risk of vulnerabilities in mobile apps to improve the security posture of your applications.
Within NIST, Appknox targets NIST 800 53 and NIST 800-171 protocols.
In addition to the GDPR and OWASP compliance, Appknox maps the security gap to the corresponding protocol for NIST.
For example, if an app transport security issue occurs in the communication protocol, Appknox maps which section of NIST the app complies with. 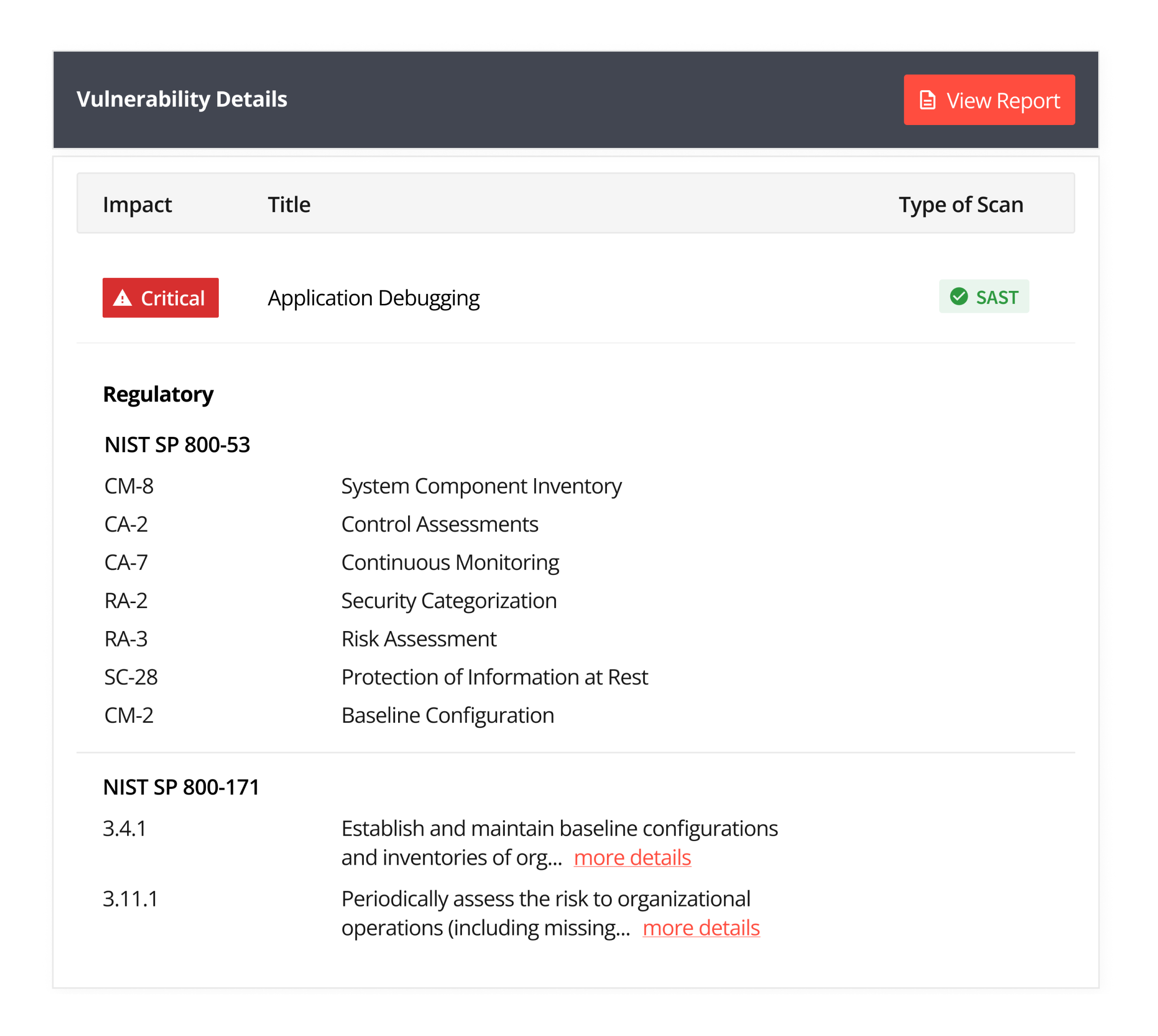
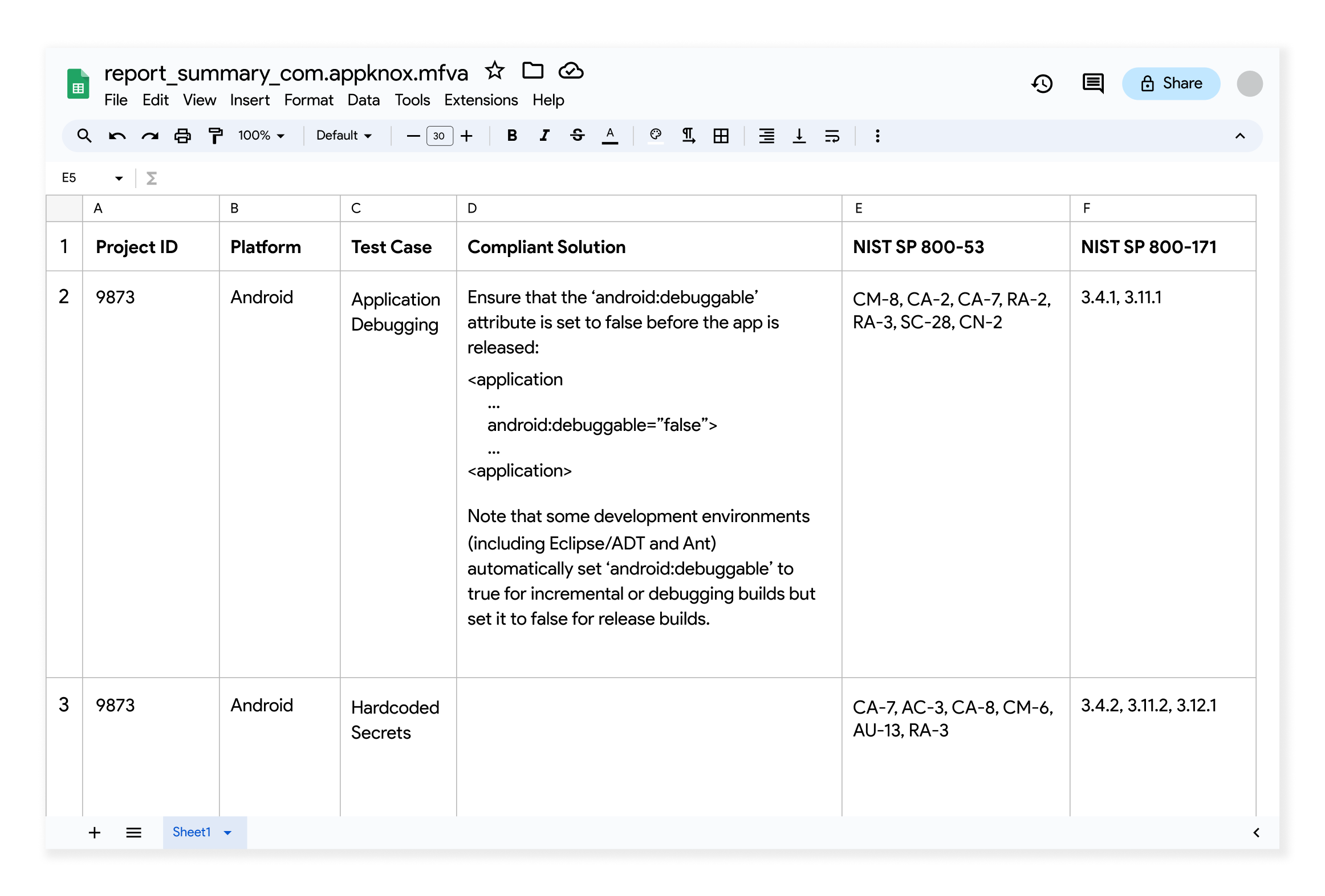
In the present-day landscape, where data privacy and integrity are paramount, Appknox goes beyond finding the security vulnerability to show which segment needs to be fixed in the compliance checklist.
Going a step further, Appknox helps with ‘criticality’ tags for detected vulnerabilities, making prioritization easier.
Appknox’s NIST compliance for mobile apps is the first step towards demonstrating your commitment to robust security practices for the evolving threat landscape, helping organizations improve their app security.
To detect vulnerabilities early in the development cycle, Appknox integrates with the application’s CI/CD (continuous integration and continuous development) processes to monitor the improvements in the security posture over time.
NIST compliance for applications ensures that the mobile app is free from vulnerabilities. Whether they’re accidentally inserted during the development lifecycle or while interacting with other systems and third-party implementations and interactions, the NIST framework gives everyone the peace of mind that their application is protected from vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
