
BLOG

BLOG
With the Internet's widespread growth, South Africa has become quite dependent on it for economic affairs. This sharing of self-generated data is a boon to all business transactions and even social interactions.
The increased dependence on the digital world raises significant concerns about cyber security.
Cybercrime is a global problem that has affected South Africa, both in the private sector and in government. Financial losses have been in the billions and could continue to increase if stricter measures are not put in place.
The main target of the African continent is mainly South Africa due to its high connectivity rate, wealth, and GDP per capita.
As per a 2014 report by the Center for Strategic and International Studies on cyber-crime, South Africa lost 0.14% of its GDP to cyber-crime.
According to the SNAI, cyber-crime costs the country over 1 billion rands ($64 billion) a year. Nearly half of these losses were due to debit card fraud. South Africa stands in 11th place (434 complaints) in terms of the most affected countries in the world.
With the rising number of cybercrimes, the government implements refined compliance regulations to safeguard its citizens and business entities. Multiple regulatory compliances have been introduced to reduce the sensitive information leakages and subsequent attacks.
The journey towards enacting cyber security compliance started long back. South Africa rightly envisaged the importance of the Internet and its pros and cons. In 2012, the South African Cabinet adopted the National Cyber Security Policy Framework (NCPF) to draw a centralized approach to ensuring the country's cyber security.
The NCPF addresses disputes among:
The NCPF sets out security guidelines in South Africa for the government to develop comprehensive cyber-security policies and strategies.
There are multiple compliance frameworks South Africa adheres to:
In South Africa, data security comes under the Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA).
On July 1, 2021, the material implementation of the most critical provisions of POPIA was enforced. This legislation promotes the protection of personal data processed by public and private bodies.
It outlines the:
It also has the power to levy penalties for breaking the law.
The safeguarding condition in the POPIA act dictates that a person must guarantee the confidentiality of personal data. It requires this to prevent loss, damage, or unauthorized access or destruction of personal data.
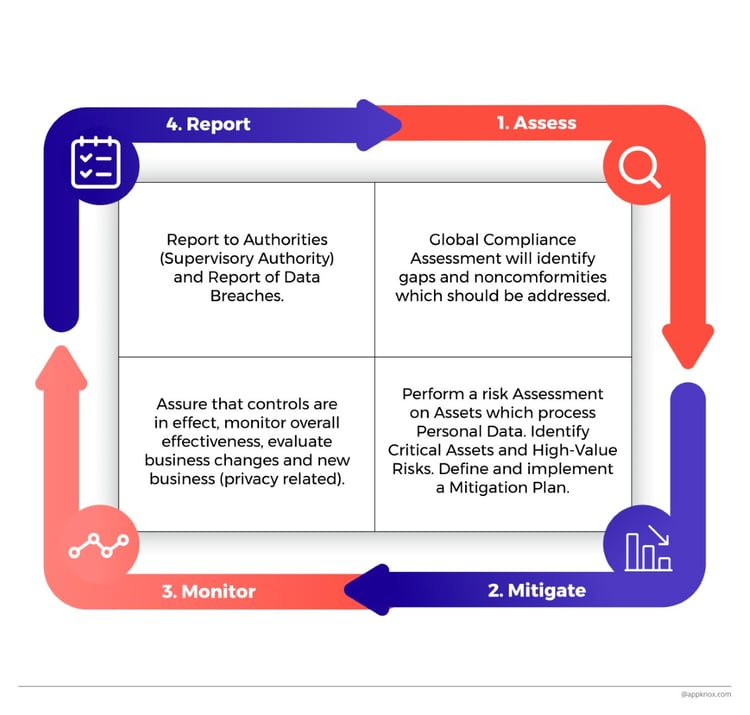
POPIA puts South Africa up to the standards with international data protection laws. This is achieved by regulating the processing of personal data of individuals and entities.
If there is reason to believe that personal data has been breached in relation to POPIA, the responsible party must notify the data controller.
In case of a data breach the business may also be subject to a:
The GDPR is a far-reaching law implemented on May 25, 2018. It obliges companies to safeguard the personal data and privacy of EU citizens residing in EU member states and regulates the export of their data outside of the EU.
In principle, the law affects all Europe companies with a digital presence.
Any company conducting business in Europe must be GDPR compliant if:
If it doesn't comply, it might risk penalties or fines of 20 million euros or 4% of its annual turnover.
The GDPR requires businesses to have clear evidence that the data subject has consented to data collection. They need to review the existing database and obtain consent from people who have never explicitly consented. If they don't get permission, they need to remove the data immediately.

A South African company needs to implement data protection through a composite data policy. They must also have a data breach notification system in place (no later than 72 hours after the breach) and appoint a data protection officer responsible for ensuring compliance.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is an information security standard for organizations. Especially for those that manage branded credit cards from major card schemes.
PCI DSS is a standard that all organizations in South Africa and online merchants. They must follow when storing, processing, and transmitting their customers' credit card information.
PCI DSS compliance is one of the most stringent and coveted security standards in the industry today. With six goals, 12 requirements, and over 300 sub-requirements, it helps organizations reduce and minimize the risk of their payment systems and cardholders' data being compromised.
PCI Certification encompasses several well-known best practices, such as:
In addition, organizations should also restrict access to cardholders' data and network resources. PCI compliance is divided into four levels. This is based on the annual number of credit or debit card transactions in business processes.
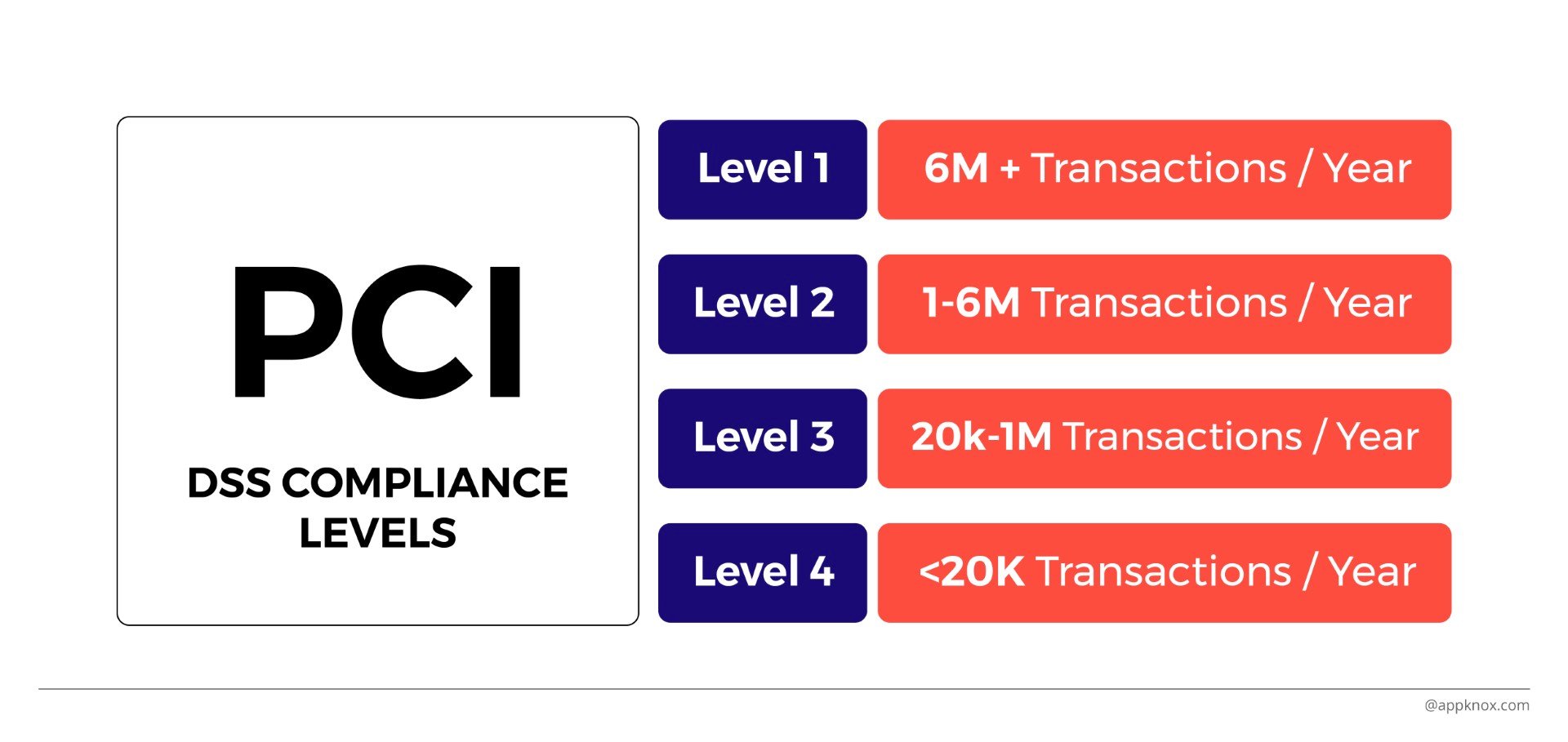
PCI compliance is a global benchmark that assures the customers about safety.
The cost of a breach, both monetary and reputational, should be enough to convince any business owner to take data security seriously. PCI is a must-have for any organization in South Africa dealing with financial transactions to ensure safety, security, and trust.
SOX (Sarbanes Oxley Act) is a law passed by the United States Congress. It requires publicly traded companies to undergo rigorous financial reporting audits and internal controls. These audits do not necessarily mean that a company has flaws in its accounting processes.
On July 30, 2002, the law was passed after scathing financial scandals involving Enron, Worldcom, Tyco International, and other high-profile companies.
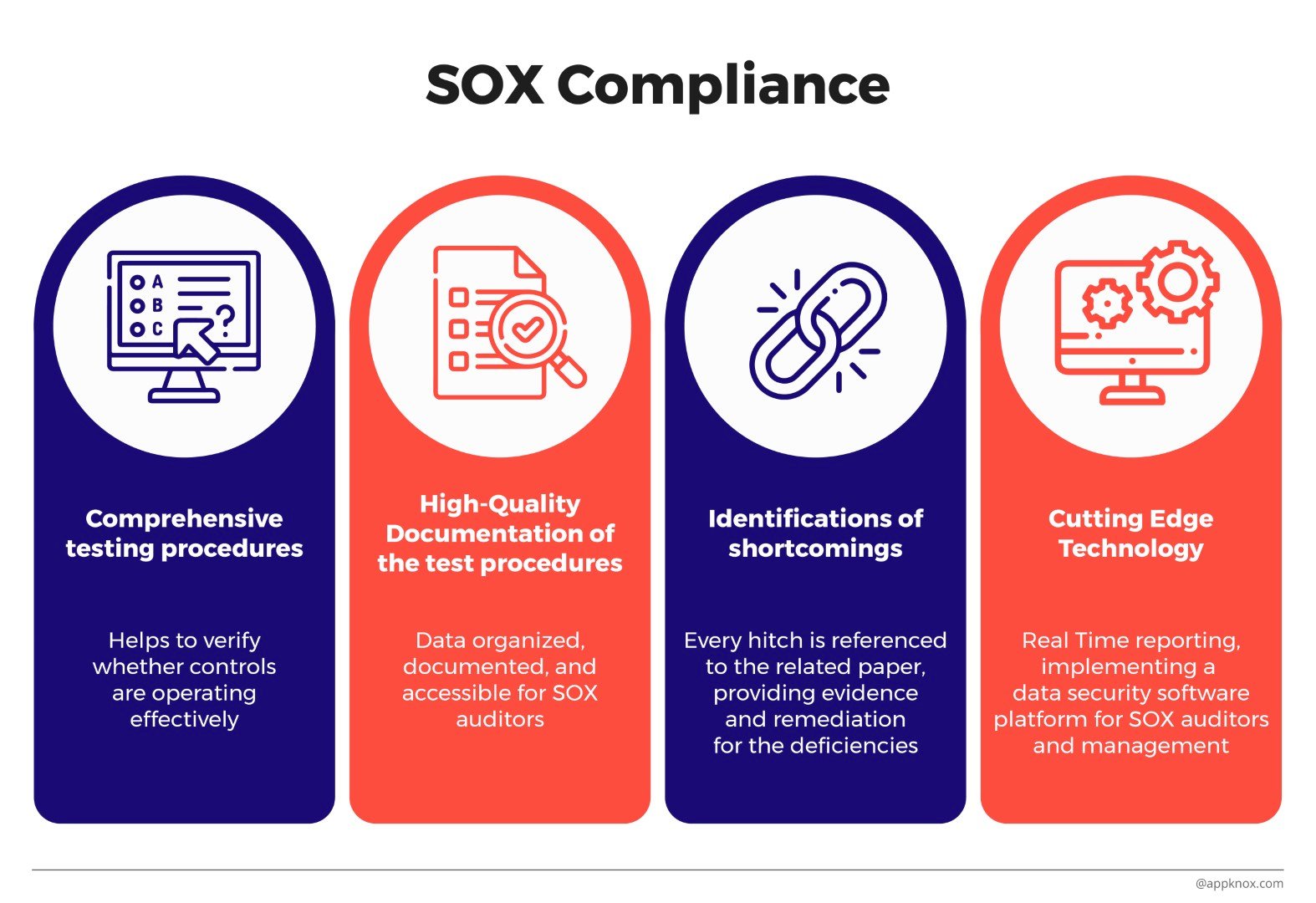
SOX was developed to implement accounting and disclosure requirements to increase transparency in corporate governance.
SOX applies to:
It requires companies to have these controls audited annually by an external company. An IT-SOX independent auditor must review controls, policies, and procedures during the audit.
A SOX IT audit examines the following high-level internal control elements:
With the growing digital dependency, the regulatory complexities are rising exponentially. It demands a significant amount of productive time for the organizations.
A single non-compliance, whether in the case of POPI or GDPR, can attract heavy monetary penalties or even sanctions and prison sentences.
In these cases, an expert can help these companies to sail through the tedious journey and save them both time and money.
Based on multiple years of valuable cyber-security experience, Appknox understands the pain points and the subsequent intricacies associated with different risk responses.
Appknox's automated security assessment has resolved security issues like data privacy and compliance flaws for 300+ enterprises, including the Fortune 500.
We will help you sail through the Assessment and Certification audits seamlessly with our extensive expertise.
Thanks to the rapid adoption of the newest technologies, South Africa is rising in the global market. Though it's great news for a young nation, it needs to go miles. To rise above the pressing challenges, it has to strive for regulatory compliance to ensure trust and safety for businesses. With these well-placed efforts, South Africa will pave the way for massive future growth and expansion in the global market.

Hackers never rest. Neither should your security!
Stay ahead of emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices in mobile app security—delivered straight to your inbox.
![]() Exclusive insights. Zero fluff. Absolute security.
Exclusive insights. Zero fluff. Absolute security.
![]() Join the Appknox Security Insider Newsletter!
Join the Appknox Security Insider Newsletter!
